Did You Know? Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Explained…
It’s easy for us to think of ears as what is externally visible on our body and perhaps something to decorate with earrings or sit our sunglasses on. However, ears are a very complex part of our anatomy and go much deeper than you may realise and work in conjunction with other parts of your body. The team at Ear Studio would like to educate and bring awareness to issues that can affect your body’s basic functioning and wellness. Let’s dive in!
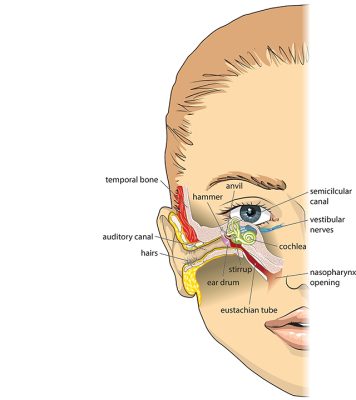
What is the Eustachian Tube?
The Eustachian tubes are small air passages that connect the middle ear (the space behind the eardrum) to the back of the nose. They are controlled by small muscles at the back of the throat.
The functions of the Eustachian tubes are:
• Balancing the air pressure in the middle ear with the air pressure in the outside environment.
• Draining fluid from the middle ear.
• Protecting the middle ear from infections and disease.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD)
This happens when the Eustachian tubes become blocked and fail to equalise the pressure of the middle ear. This can cause a feeling of fullness and your hearing can seem muffled. If the tube remains blocked for a long time this may cause inflammation of the middle ear and eventually an infection. Symptoms
• A feeling of fullness or ‘blocked’ ears.
• Crackling or clicking sounds when chewing or swallowing.
• Ear pain or discomfort.
• Muffled hearing.
Causes
ETD is often caused by differences in air pressure arising from:
• Altitude changes (air travel, driving through hilly environments, scuba diving).
• Nasal congestion, sinus problems or allergies.
• The common cold; chest, ear, or sinus infections.
This is made by a doctor or audiologist, either by physical examination or use of a specialised machine called a tympanometer. The ear drum might appear retracted (sucked further into the ear). Measuring the middle ear pressure via the tympanometer confirms the diagnosis and can be used as a follow up tool to check the progress of the problem.
Treatment
If the dysfunction is mild, often no treatment is required, and the symptoms usually resolve within a few weeks.
Treatments may include:
• The Valsalva manoeuvre, which involves exhaling forcefully through your nose while pinching it shut with your fingers and keeping your mouth closed. This is used to equalise air pressure between the middle ear and the outside environment.
• Chewing gum to activate the muscles that control the Eustachian tubes.
• Nasal decongestants or antihistamines can assist with clearing the eustachian tube and nasal passages. • Special earplugs can help regulate pressure changes during flights.
• Surgical intervention may be discussed if noninvasive treatments fail.
At Ear Studio, uncompromising approach is what makes our hearing clinic unique, and different to other hearing health providers. This ensures we deliver positive and consistent hearing and ear health outcomes.
Please give our friendly staff a call on 02 9159 6122 to book your appointment today. Or you can head to our website www.earstudio.com.au and book your appointment through our online booking system.











